Beyond the Newsroom: 10 Cutting-Edge Innovations at Arm in July 2024
The Arm Editorial Team is constantly looking for the most intriguing and cutting-edge technology trends and stories. In this edition of “Beyond the Newsroom,” we talk about various groundbreaking innovations and developments involving Arm in July 2024.
From outperforming benchmarks and transforming IoT machine learning (ML) to wildlife conservation and revolutionizing mobile gaming, Arm is pushing the boundaries of what’s possible in the tech world.
Revolutionizing mobile gaming performance
The Arm Accuracy Super Resolution (Arm ASR) is a new open-source solution for upscaling mobile devices. Peter Hodges, Director Developer Ecosystem Strategy at Arm, elaborates on how Arm ASR improves GPU performance, reduces power consumption, and maintains high-quality graphics.
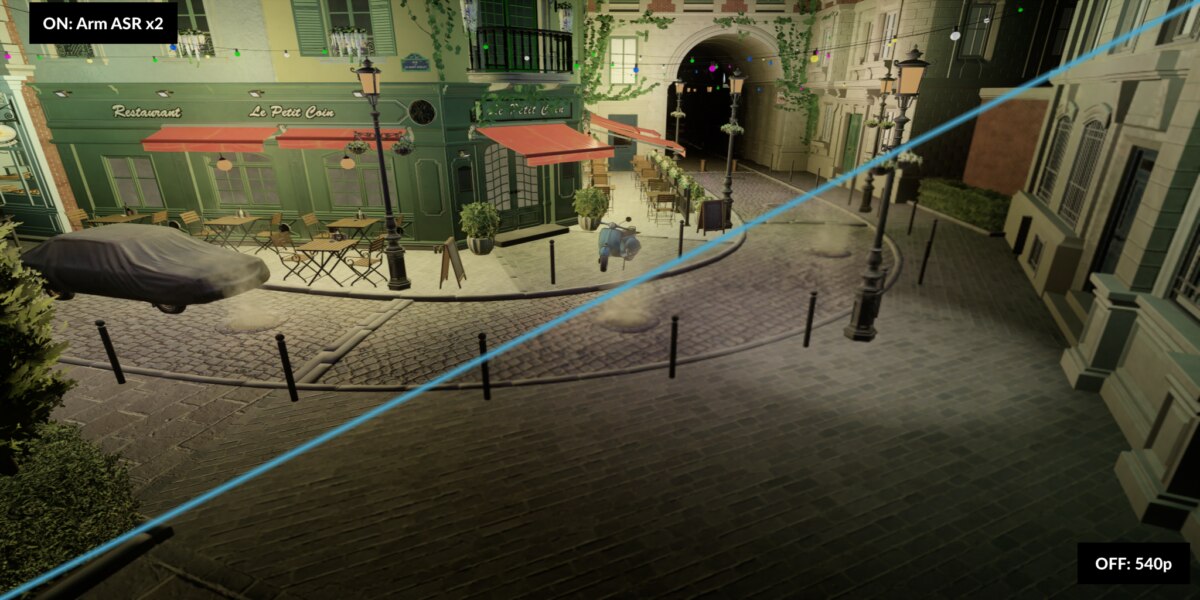

Arm ASR uses temporal upscaling, which combines information from multiple frames to produce higher-quality images from lower-resolution targets. The technology can lead to longer battery life and stable temperatures on mobile devices, while also addressing common graphical performance challenges. This enables game developers to create more complex and visually appealing games without compromising performance.
Meanwhile, Syed Farhan Hassan, Software Engineer at Arm, talks about how Arm created a demo using Unreal Engine to show how Android Dynamic Performance Framework (ADPF) optimizes game performance. The demo also showcased how ADPF helps developers optimize application performance by a whopping 57 percent. This is achieved by adjusting graphics settings like shadow, reflection, and texture quality to prevent thermal throttling without a noticeable impact on gameplay.
Yitian 710 outperforms Ice Lake in Apache Flink benchmarks
Apache Flink is a framework for stateful computations over bounded and unbounded data streams, which utilizes a distributed streaming data-flow engine written in Java and Scala. Bolt Liu, Staff Software Engineer at Arm, shows the performance benchmark when comparing Yitian 710 (Neoverse N2) and Ice Lake using the Nexmark data stream benchmark tool on a Flink cluster with identical hardware and software configurations.
The results showed that the Yitian 710 significantly outperformed Ice Lake in high-throughput query tests, with improvements of over 30 percent in most cases and up to 83 percent in some others. The superior performance of Yitian 710 in these high-throughput scenarios highlights its benefits for demanding data stream applications, with this suggesting strong potential for future deployments in data-intensive environments.
Transforming IoT ML with TinyML and Ethos-U55 NPU
TinyML focuses on deploying ML models to low-power, resource-constrained IoT devices, enabling on-device data processing. Sandeep Mistry, Principal Software Engineer and Developer Evangelist in Arm’s IoT Line of Business, discusses how this approach reduces latency and preserves privacy by processing data locally on the device without needing to send it to the cloud.
Arm’s Ethos-U55 NPU significantly accelerates ML model inference, allowing complex models to run efficiently on microcontrollers. Additionally, offloading ML computations to the NPU enables applications, such as face and pose detection, to perform multiple inferences per second, which can enhance responsiveness to the environment.
Contributing towards wildlife conservation with AI for Bears Challenge
Arm joined forces with FruitPunch AI to sponsor the AI for Bears Challenge – an initiative that applies AI to support wildlife conservation, specifically for monitoring bears. Ed Miller, Senior Principal Engineer at Arm, discusses how the participants used Arm Virtual Hardware and the NXP i.MX93 development platform to help develop AI models for bear detection and identification.
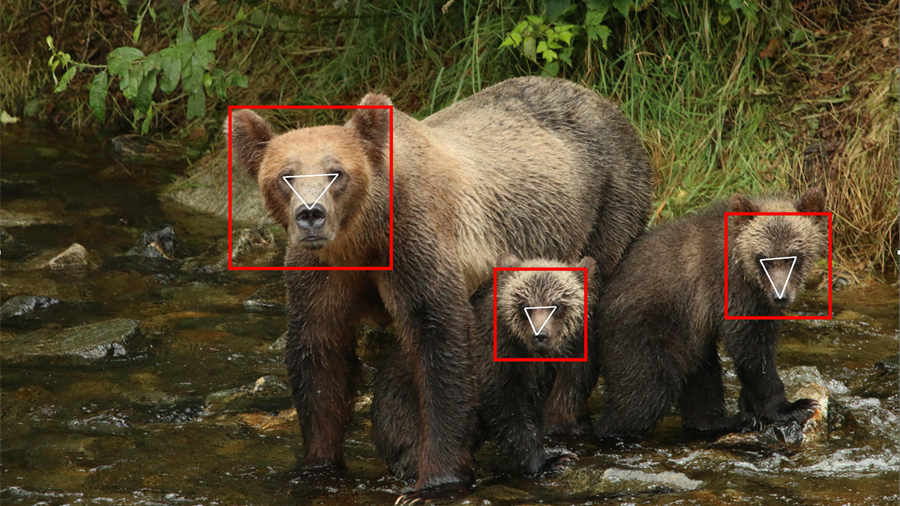
The initiative not only achieved significant speedups and power savings, but also provided near real-time AI solutions for wildlife monitoring. Moreover, the project contributed to conservation efforts, reduced human-bear conflicts, and inspired participants to pursue AI for Good.
Setting new benchmarks in performance and cost efficiency with AWS Graviton4 on Arm
Tim Thorton, Director, Arm on Arm, talks about the AWS Graviton4, which is based on the Arm Neoverse V2 core, and how the AWS Graviton processors have evolved from Graviton2 to Graviton4 – with each generation offering significant performance improvements. Now, over half of compute-intensive register transfer level (RTL) simulations run on AWS Graviton-based EC2 instances.
Graviton4 is nearly twice as fast as Graviton2 and offers the best price/performance ratio in the memory-optimized R instance family. Additionally, Graviton4 enables a broader range of EDA applications, making it the optimal platform for various workloads. It also allows x86-based instances to be turned off for some performance-sensitive tasks.
Enabling smart and energy-efficient ML edge devices on Arm
Reinhard Keil, Senior Director, Embedded Technology at Arm, discusses how Arm is enabling developers to create smart, energy-efficient ML edge devices by integrating AI with IoT endpoints, allowing real-time data processing and localized control. ML applications on edge devices can be optimized through various Arm processors, such as Cortex-M0/M0+, Cortex-M4, and the Helium vector extension on Cortex-M52, M55, or M85.
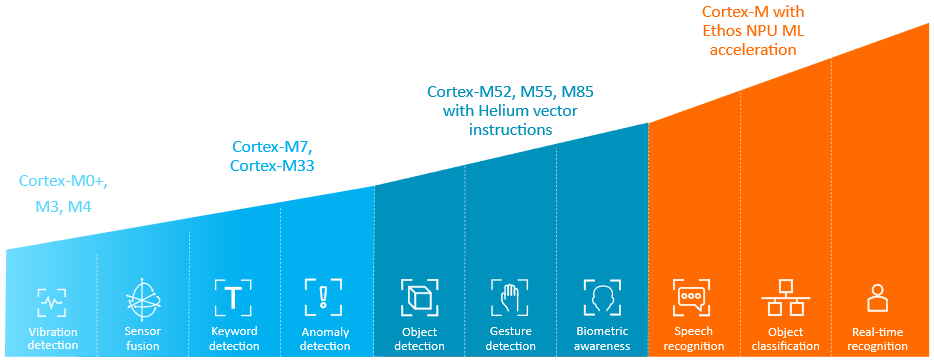
Moreover, Arm’s Corstone IoT sub-systems, like Corstone-315, can accelerate the development of ML edge devices by offering architecture choices, integration, as well as verification support. Keil also emphasizes the importance of software standardization, development tools, and ecosystem partnerships, with tools, like the Common Microcontroller Interface Standard (CMSIS), and ML frameworks, like TensorFlow, validated for Arm processors.
Arm offers a comprehensive ML Developers Guide for Cortex-M Processors and Ethos-U NPU, covering the entire ML development workflow from model training to hardware debugging, supported by evaluation boards and simulation models.
Enhancing DTVs user experience with edge-based speaker identification technology
Marcus Corbin, Graduate Engineer at Arm, discusses how speaker identification technology, based on deep neural networks (DNNs) on Arm-powered Digital Televisions (DTVs), can enable personalized and secure interactions with DTVs. This is achieved by running AI workloads on the DTVs to improve data privacy, as well as reducing latency when compared to other cloud-based solutions.
The TitaNet Small model is found to offer a good balance between model size and accuracy, with efficient inference times even on resource-constrained devices. The technology can allow for personalized interactions with DTVs by recognizing who is speaking, offering a seamless and optimized user experience.
Innovation Coffee with Michael Hall and Robert Wolf
Join Michael Hall and Robert Wolf on Innovation Coffee as they dive into the exciting new GitHub Action Runner on Arm64, its development journey, and the benefits it brings to developers and the open-source community. They are joined by Arm’s Diego Russo and GitHub’s Larissa Fortuna.
In another Innovation Coffee video, Robert and Michael talk about the latest happenings across the Arm developer ecosystem – from events like Open Sauce in San Francisco to insightful learning paths on Microsoft Sandbox and confidential computing on Arm CPUs.
Create an Orca Mini and Phi 3 chatbot with Python running locally on a Raspberry Pi 5
In this YouTube video, Arm’s Gabriel Peterson explains how to set up a local large language model (LLM) chatbot on a Raspberry Pi 5 using the Orca Mini 3B model. It covers the installation of the operating system, downloading necessary packages, and creating a Python virtual environment. The video also demonstrates how to modify the setup to run Microsoft’s Phi-3 LLM, highlighting the differences in memory usage and performance between the two models.
Unleashing the Potential of the Arm Architecture
In his keynote at the We Are Developers event, Arm’s Andrew Wafaa discusses how software developers can unleash the full potential of the Arm architecture as part of the mission to “write once, deploy anywhere.” Andrew highlights the importance of software in maximizing the capabilities of Arm’s pervasive computing architecture, which spans from cloud to edge devices. He also emphasizes the tools and libraries available to developers, such as the new Arm Kleidi software, performance studio, and virtual platforms, as well as Arm’s significant open-source investments.
Any re-use permitted for informational and non-commercial or personal use only.













