Arm and AWS Demonstrate Cloud-native Automotive Development with SOAFEE
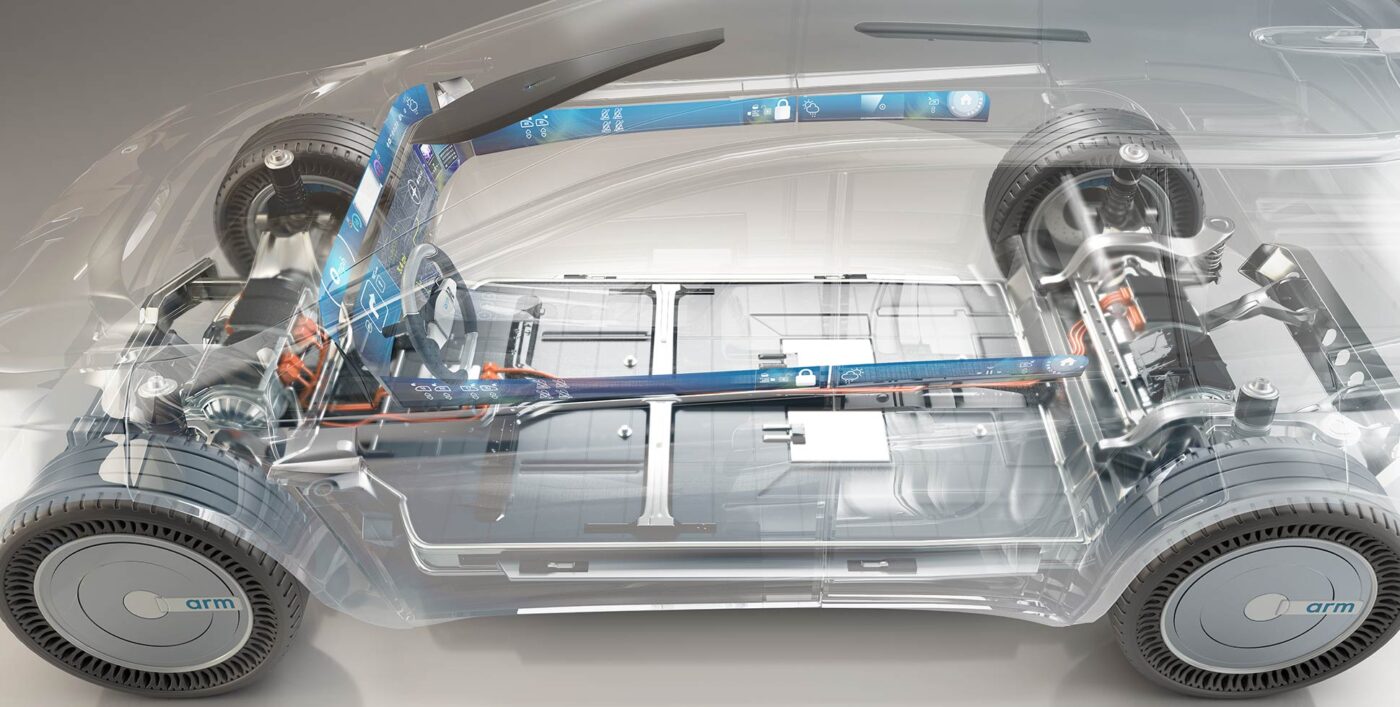
Cloud-native automotive development means moving to a cloud-based paradigm in which software is developed in the cloud and deployed directly to a software-defined vehicle at the edge.
Developers are able to build and test software workloads from anywhere: in the office, working from home, even working from a café, and then deploy them securely to the vehicle.
SOAFEE—the Scalable Open Architecture For the Embedded Edge—is an open-standards-based architecture designed to facilitate cloud-native automotive development. Launched in September 2021, SOAFEE is backed by industry leaders including Arm, AWS, Bosch, CARIAD, Continental, Red Hat, Suse, and Woven Planet.
To demonstrate SOAFEE in action, Arm and AWS have created a demo using automotive workloads, being developed and tested in the cloud and then deployed to the edge, showcasing its significant benefits to the automotive industry.
The demonstration showcases cloud-native automotive development using what we call ‘environmental execution parity’ by seamlessly moving the same workload between the cloud and a software-defined vehicle at the edge, enabling rapid development and deployment of software-defined automotive functions.
Environmental execution parity
Software-defined vehicles will use heterogeneous compute architectures consisting of powerful CPUs alongside accelerators, which will often be GPUs. For a cloud-native automotive development workflow to be most effective, developers can take advantage of the same compute architectures in both the cloud and the vehicle at the edge. We call this ‘environmental execution parity’.
Environmental execution parity removes the compromises and inefficiencies involved in developing on a different architecture in the cloud to the one being deployed to a software-defined vehicle at the edge. Cross-compilation of code is no longer necessary, speeding up the build process and removing a source of potential error. Testing of workloads carried out in the cloud now correlates closely with the results that would be seen when running the workload in the vehicle.
Environmental execution parity for automotive development experienced a major breakthrough when AWS recently announced its new Amazon EC2 G5g instances, pairing powerful Arm Neoverse-based Amazon Graviton2 processors with NVIDIA T4G Tensor Core GPUs. Developers can now gain easy access to the right compute mix for automotive development in the cloud, essential for high performance and mixed-criticality systems in software-defined vehicles.
Arm and AWS demonstrate cloud-native automotive development using SOAFEE
The demonstration by Arm and AWS makes use of these new Amazon EC2 G5g cloud instances for cloud development, alongside an ADLINK AVA Automotive Developer Platform which pairs Arm Neoverse-based processors from Ampere with an NVIDIA RTX5000 GPU. This combination provides developers with environmental execution parity across the cloud and the car, a compelling development experience that will accelerate cloud-native development for automotive applications.
This is just the first foundational step in the modernization of the automotive industry through cloud-native automotive development. The software stack uses existing cloud-native technologies, but extra capabilities are required. Functional safety is a key requirement to ensure the well-being of drivers, passengers, and the environment surrounding the car.
Automotive workloads can be mixed-critical, with safety and real-time characteristics, meaning some require a higher level of criticality than in traditional cloud development. The SOAFEE Special Interest Group (SIG) has now been formed to define and implement the architecture that will add these capabilities to cloud-native software stacks.
Building on the workshop hosted at Arm Dev Summit in October, the Arm and AWS demo shows an example object-detection workload hosted in a container and running on the Arm-based CPUs in both the G5g running in the Cloud and AVA platform at the edge, both running with the support of Nvidia GPUs.
AWS services are used to create a Continuous Integration / Continuous Development (CI/CD) pipeline to build, containerize, evaluate and enable the deployment, whether developing in the cloud or on the AVA development platform at the edge.
All of this will foster collaboration and innovation through the automotive value chain. Virtualized machine images can be distributed to partners to develop and test applications and workloads in the cloud which can then be integrated into the development of specific car models and features and deployed to production vehicles.
With this new automotive development paradigm, the automotive industry will be able to efficiently and effectively deliver the software-defined car, the future of mobility that will result in new experiences for us all.
Together, Arm and AWS are showing the way forward for cloud-native automotive development and the software-defined vehicle. AWS Graviton-powered cloud services and the SOAFEE architecture speed software development, testing, and deployment.
Delivering a software-defined future
The evolution from hardware-defined to software-defined compute requires new development paradigms to ensure seamless deployment from the cloud to the car. Arm and our partners are committed to making this a reality.
Any re-use permitted for informational and non-commercial or personal use only.













