Top Arm-based innovations from December 2025 and January 2026

As 2025 closed and 2026 began, innovation across the Arm ecosystem continued at pace. From cloud and automotive platforms to edge AI, gaming, and even space-grade systems, the pace and breadth of recent innovation show how Arm-based technologies are being adopted and expanded across real-world deployments.
Across industries, partners and developers are pushing boundaries, with the Arm compute platform being used to scale performance, unlock new levels of efficiency, and bring powerful capabilities closer to users. What we’re seeing isn’t incremental progress, but a clear signal of how Arm is enabling the next wave of computing, turning advanced ideas into experiences that are faster, smarter, and more accessible.
SpaceX to use Arm-powered STMicroelectronics’ microcontrollers in Starlink
STMicroelectronics has announced a new Arm-based STM32 microcontroller built on an 18nm process with embedded phase-change memory, which is designed for use in space and other high-reliability environments.
The integration of advanced non-volatile memory enables greater on-chip capability, long-term data retention, and software flexibility in systems that must operate for years without maintenance. This milestone highlights how Arm-powered microcontrollers are supporting mission-critical applications where resilience, efficiency, and longevity are essential.
Scaling Microsoft Defender for Endpoint cloud security with Arm-based Azure Cobalt processors
Microsoft Defender for Endpoint is a cloud-native security service designed to detect and respond to threats across large numbers of devices worldwide.
In this video, Richard Murillo, Software Engineering Manager for Microsoft Threat Protection, describes how the platform operates one of Microsoft’s most demanding cloud workloads. He explains how Defender for Endpoint is built on cloud-native microservices running on Azure Kubernetes Service, and why Arm-based Azure Cobalt processors are being used to support high-throughput, scalable security analytics.
How transformer models are moving from the cloud to the edge
AI models that were once designed mainly for large cloud systems are now being adapted to run closer to where data is created. This shift makes it possible to deliver real-time intelligence on devices with limited power and computing resources.
In this Arm Community blog, Alexey Vilkin, Staff Software Engineer at Arm, explains how to take a speech-recognition model from training to deployment. He walks through training and optimizing a Conformer model using PyTorch, then shows how it can be efficiently deployed on the Arm Ethos-U85 NPU. The guide demonstrates how careful model optimization can maintain high accuracy while fitting within the tight limits of edge devices.
Accelerating on-device ML with ExecuTorch and Arm SME2
ExecuTorch is a lightweight, mobile-first runtime designed for deploying PyTorch models efficiently on edge devices, while Arm Scalable Matrix Extension 2 (SME2) boosts matrix processing throughput for AI workloads on Armv9 CPUs.
In this Arm Community blog, Jason Zhu, Senior Principal Engineer, shows how combining ExecuTorch with SME2 significantly speeds up inference for transformer and convolutional models. Discover how this software–hardware pairing delivers faster, more responsive on-device AI—without sacrificing efficiency—making it well suited for real-time, edge-based applications.
Samsung Exynos 2600 advances on-device AI with Arm technology
Samsung has announced the Exynos 2600, a new processor built on Arm technology that brings improved on-CPU machine learning (ML) to next-generation devices.
Built on Arm Compute Subsystems (CSS), using the Arm C1-Ultra CPU, Arm C1-Pro CPU, and SME2, the platform is designed to support faster and more efficient on-device AI. This enables lower-latency processing and expands the range of AI experiences that can run directly on devices.
How Synopsys and Arm are shaping AI-driven vehicle platforms
Synopsys provides software, intellectual property, and engineering services that support the design of advanced chips and electronic systems used across consumer, data center, and automotive applications.
In this video, Ravi Subramanian, Chief Product Management Officer at Synopsys, explains how Synopsys and Arm are working together to improve the development of automotive computing platforms. He also outlines how the combination of validated Arm CSS with Synopsys IP and virtual prototyping tools helps automakers design, test, and refine AI-enabled silicon more efficiently. This approach supports faster development of software-defined and AI-driven vehicles, while improving the path to new intelligence and safety features.
Xbox app now available on Windows on Arm
The Xbox app has been released for Arm-based Windows 11 devices, giving players access to a growing catalog of PC games. Around 85% of Game Pass titles are already compatible on Arm, broadening the range of games that can run natively on these systems.
Developed in collaboration with Microsoft and ecosystem partners, this update expands choices for PC gamers using Arm-based hardware.
Arm Development Studio 2025.1 accelerates debug and optimization for C1-family designs
Arm Development Studio 2025.1 now brings full support for the new Arm C1‑family of CPUs, including the Arm C1‑Nano, Arm C1‑Premium, C1-Pro and C1‑Ultra, alongside expanded tooling that accelerates bring‑up, debugging, and performance optimization of next‑generation designs.
In this Arm Community blog, Lukas Snetler, Senior Product Manager at Arm, details how updated toolchains, enhanced debuggers, high‑fidelity virtual platforms, and deeper performance insights help developers start earlier, see more, and tune systems with greater confidence. Whether you’re targeting cutting‑edge mobile systems-on-chip (SoCs) or advanced embedded systems, this release allows developers to keep pace with the latest Arm IP and shortens the path to success.
Google Cloud N4A powered by Arm Neoverse N3 is now generally available
Announced last year, Google has now made its N4A instance type generally available on Google Cloud. Built on Arm Neoverse N3 cores with Google’s Axion architecture, N4A offers improved price-performance for cloud-native workloads.
With support from the broader Arm ecosystem, this option helps customers scale more efficiently and optimize total cost of ownership for demanding cloud applications.
Edge AI brings real-time fall detection to elderly care
Real-time fall detection uses AI to instantly recognize when a person has fallen, triggering alerts without human intervention. In elderly care settings, this capability can be life-saving, especially when deployed directly on-device.
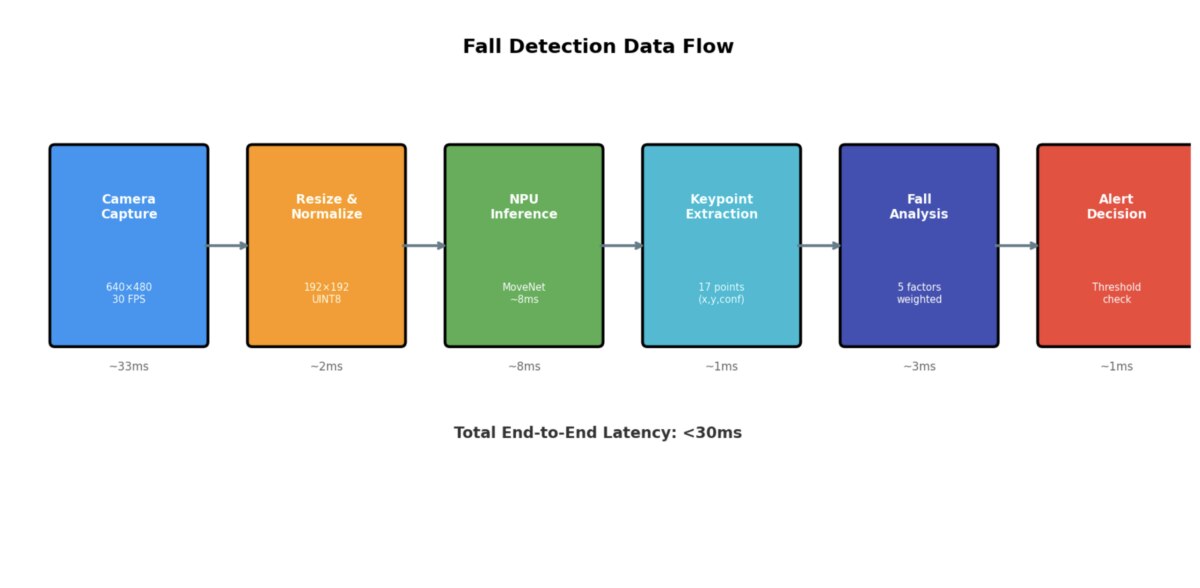
In this Arm Community blog, Fidel Makatia, a PhD student at Texas A&M University and Arm Ambassador, showcases an open-source edge AI system that runs real-time fall detection using the Arm Ethos-U65 NPU. By processing sensor data locally, the system enhances privacy, reduces latency, and operates continuously with low power.
Hands-on with edge AI and Raspberry Pi 5
Low-latency AI powers real-time, on-device decision-making; no cloud required. In a project from Dominic Pajak, Senior Director in Arm’s Edge AI Business Unit, Hugging Face models run locally on an Arm-based Raspberry Pi 5 to enable responsive, human-like interaction with the Reachy Mini robot.
Built using accessible hardware and edge AI techniques, developers can prototype intelligent, interactive systems that respond instantly in the real world.
NUMA-aware tuning on Arm servers scales Llama.cpp performance
Cross-NUMA memory access occurs when a processor core retrieves data from a memory bank attached to a different NUMA (Non-Uniform Memory Access) node, often leading to increased latency and reduced throughput in multi-threaded workloads.
In this Arm Community blog, Bolt Liu, Staff Software Engineer, details how optimizing llama.cpp on Arm Neoverse N2 platforms using NUMA-aware thread pinning and weight balancing delivered up to 55% faster text generation.
Any re-use permitted for informational and non-commercial or personal use only.











