Top 12 innovations from Arm in October 2025
AI innovation is accelerating faster than ever and in October 2025, Arm was at the center of that momentum. From unlocking neural rendering for next-gen gaming to driving smarter cloud efficiency, the month showcased how Arm’s ecosystem continues to push what’s possible across every layer of compute.
The Arm Editorial team have highlighted the top innovations from Arm in the past month and how we are enabling developers, OEMs, and cloud providers to build more intelligent, efficient, and scalable systems, spanning edge devices, automotive platforms, data centers, and creative tools
Bringing AI to the edge with ExecuTorch 1.0
Arm and Meta’s open-source inference engine, ExecuTorch 1.0, is now generally available and marks a major milestone in making AI truly on-device. Built to run efficiently across Arm CPUs, GPUs, and NPUs, ExecuTorch enables developers to deliver low-latency, power-efficient AI experiences directly on edge devices, from microcontrollers to flagship smartphones.
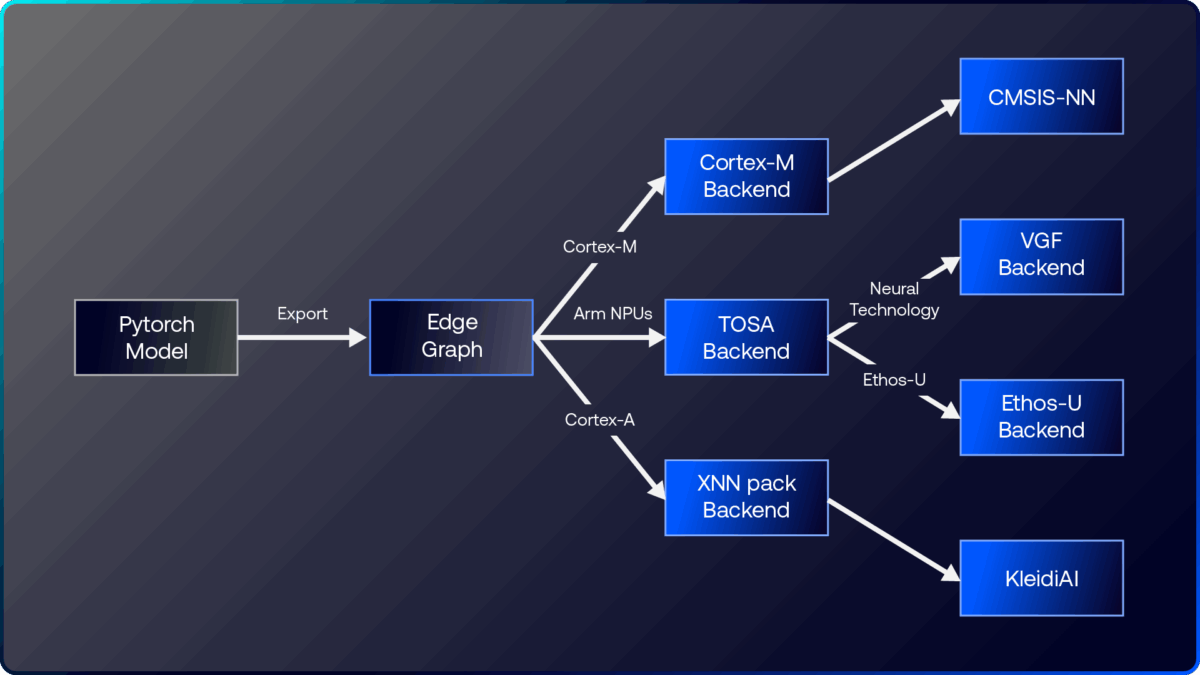
Gian Marco Iodice, Principal Software Engineer, details how Arm Scalable Matrix Extension 2 (SME2) brings next-generation matrix processing efficiency to Arm CPUs to dramatically boost AI inference performance. Meanwhile, Robert Elliott, Director of Applied ML, explores Arm Neural Technology’s role in scaling inference across modalities. Finally, Fredrik Knutsson and Per Åstrand, Principal Engineers and Team Leads, demonstrate how ExecuTorch unlocks AI acceleration on the Ethos-U NPU family. Together, they show how Arm is redefining edge intelligence for a world built on AI.
Built on Arm: Google Cloud
Google Cloud is helping transform the automotive industry by providing the data, AI, and infrastructure needed to build smarter, safer, and more connected vehicles. In this video, Steve Basra, Automotive Lead at Google Cloud, shares how the company is working with Arm to power the next generation of software-defined and AI-defined vehicles.
Together, Arm and Google Cloud are helping OEMs and developers bring intelligent mobility to life by combining Arm’s high-performance, energy-efficient computing with Google Cloud’s AI and data capabilities.
LLMs go on-device for mobile gaming
Arm’s latest advancement in mobile AI shows how large language models (LLMs) can now run directly on smartphones, thanks to Arm CPUs, KleidiAI, and Unreal Engine’s Neural Network Engine (NNE). This combination brings real-time conversational intelligence to games, without needing a network connection.
Bhanu Arya, Senior Software Engineer, introduces Space Bartender, a sci-fi demo featuring a responsive NPC that listens and talks naturally with players. It uses Whisper for voice input and a fine-tuned SmolLM2 model quantized to 4-bit for efficient on-device inference. With KleidiAI optimizations via ONNX Runtime, performance improves by 2.3x while maintaining low power consumption. The project signals a new era for mobile gaming, where AI-driven characters feel alive, and all intelligence stays on the device.
Built on Arm: vivo X300 Series
The vivo X300 series is vivo’s most advanced flagship smartphone to date, and built on the Arm compute platform featuring the latest CPU and GPU technologies.
In this video, Eric Xia, Chief Chipset Planning Expert at vivo, talks about the new vivo X300 series and how it uses Arm Scalable Matrix Extension 2 (SME2) technology to deliver powerful AI acceleration across vision, speech, and text workloads.
Training neural graphics with Arm Model Gym
Arm’s new Model Gym is a developer toolkit that makes it easier to train and deploy neural graphics models, machine learning systems that enhance real-time rendering through AI. By blending PyTorch-based model training with Arm’s hardware-aware inference pipeline, it allows developers to experiment with neural super-sampling (NSS) and other ML-driven visual techniques directly on Arm-based devices.
Annie Tallund, Solutions Engineer, talks about how Model Gym supports end-to-end workflows, from training and quantization to exporting models in a format ready for integration into game engines. This approach lets developers achieve high-quality visuals at lower compute and power costs and paves the way for more AI-assisted graphics on mobile and embedded platforms.
Built on Arm: Black Sesame
Black Sesame Technologies Inc. develops AI chips used in self-driving cars, advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS), and robots.
In an era in which autonomous driving is developing rapidly, Rock Yang, Chief Marketing Officer at Black Sesame Technologies, discusses how the company is working with Arm, leading OEMs, and Tier-1 suppliers around the world to help move accelerate the development of advanced in-car technologies.
Introducing AI tools that simplify cloud migration
Following the launch of the Arm Cloud Migration Assistant for GitHub Copilot, Arm has introduced the MCP Server, a new step forward in making cloud migration faster and more developer-friendly. Built on the open Model Context Protocol (MCP), the server integrates directly into AI assistants and allows developers to perform image inspections, code analysis, and architecture validation through natural language commands.
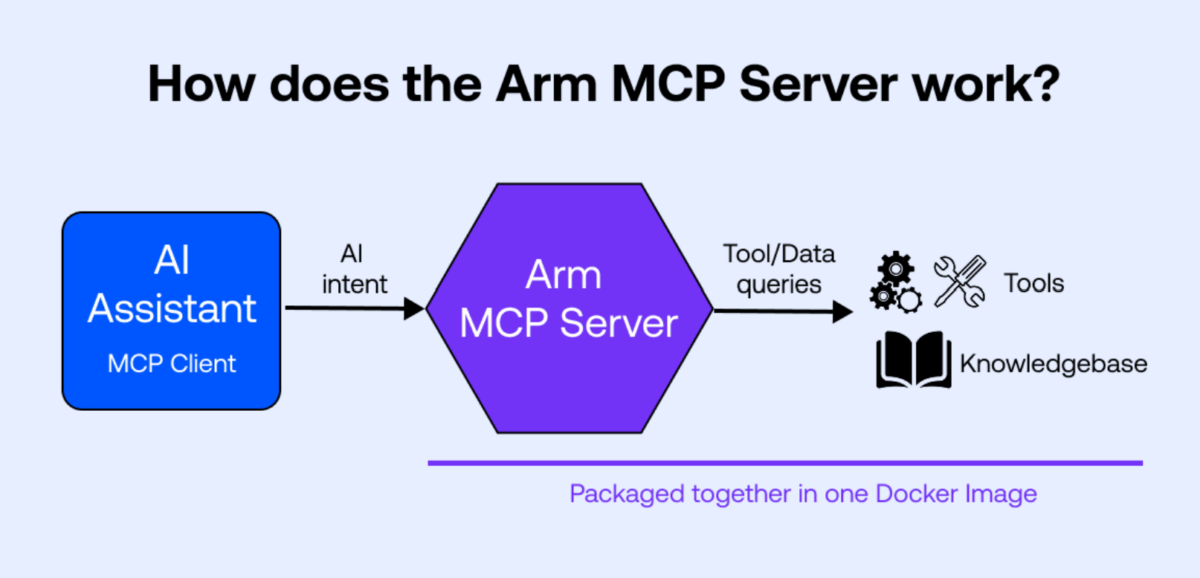
Zach Lasiuk, Principal Solutions Designer, explains how the MCP Server streamlines migration from x86 to Arm-based platforms like Microsoft Cobalt, AWS Graviton, and Google Axion. Embedding migration tooling into AI workflows helps removes manual effort and enables faster, more efficient modernization for both cost-optimized and performance-driven cloud environments.
Built on Arm: Alif Semiconductor
Reza Kazerounian, President & Co-Founder of Alif Semiconductor, shares how the company is redefining intelligent edge computing with next-generation embedded controllers and processors designed for smart homes, healthcare, wearables, and connected devices.
Built on Arm technology, Alif delivers powerful, energy-efficient silicon that supports the shift from traditional AI to generative AI. With the Arm Ethos-U85 NPU, Alif is enabling high-performance, low-power on-device AI and ML applications.
AI rendering for next-gen gaming with Arm Neural Graphics SDK
Arm’s new Neural Graphics Software Development Kit (SDK) brings AI-powered rendering, including Neural Super Sampling (NSS), to game engines, alongside a dedicated Unreal Engine 5.4 plugin that integrates real-time neural upscaling into developer workflows. Together, they enable console-level graphics on mobile and embedded devices with far greater efficiency.
Willen Yang, Senior Software Technology Manager, details how the SDK offers open-source models, Vulkan ML support, and an engine-agnostic design inspired by FidelityFX. The UE5.4 plugin uses Unreal’s temporal upscaler interface for seamless adoption across projects, marking a key step toward neural rendering as standard in mobile gaming and preparing developers for future Arm GPUs with built-in AI acceleration.
Accelerated inference on Arm Neoverse through ONNX Runtime
ONNX Runtime, enhanced with KleidiAI optimisations, now delivers LLM inference at scale on Arm Neoverse N2-based Microsoft Cobalt 100 CPU infrastructure. The stack supports multiple precision formats with no code changes required, enabling cost-efficient, high-performance CPU-based GenAI deployment.
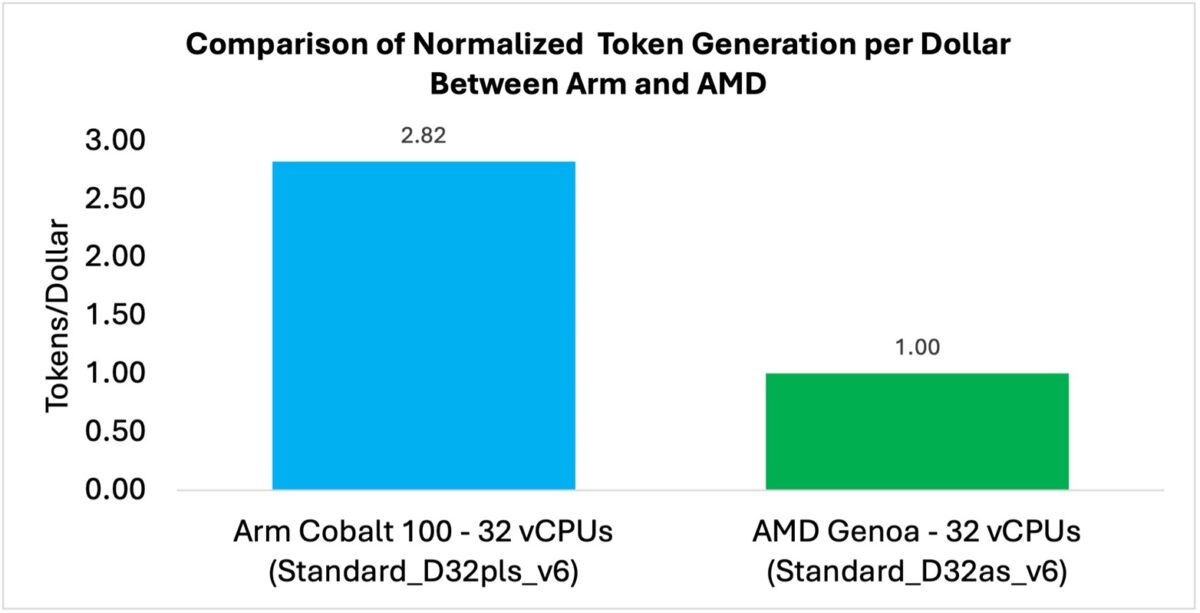
In benchmarks with the Phi-4-mini-instruct model, Na Li, Principal Solutions Architect, Nobel Chowdary Mandepudi, Software Engineer, and Koray Ozkal, Senior Manager, Infrastructure Product Marketing, explains how the Cobalt 100 and ONNX Runtime stack achieved up to 1.9x higher throughput and 2.8x better performance-per-dollar compared to an AMD Genoa x86-based instance.
This means cloud-scale LLM services can use Arm-based compute to deliver more capacity, lower power and better economics, aligning directly with both “cost-down for mass” and “feature-up for premium” strategies.
Inside the tech making low-light mobile photos look brilliant
Real-time neural-camera denoising on Arm-based devices uses AI to instantly clean up grainy or low-light images, making photos and videos look clearer and more natural.
David Packwood, Principal Computer Vision Architect, explains how Arm SME2 enables this capability by combining wide‑SIMD and matrix‑multiplication compute in the CPU. The result is a cleaner, sharper stills and smoother video (even at 4K) under the toughest lighting conditions, and a more flexible camera pipeline for phone makers.
Arm A-Profile architecture developments 2025
Arm’s A-Profile architecture powers the high-performance spectrum from mobile to hyperscale. In 2025 the firm introduced the update known as Armv9.7-A, preserving backward compatibility while advancing features around scalability, efficiency and security.
Martin Weidmann, Director, Product Management, introduces features such as targeted memory invalidation broadcasts, enabling the OS or hypervisor to invalidate TLB entries only for specific domains in multi-chiplet systems, reducing latency and improving coherence. For OEMs and silicon designers, this unlocks more efficient multi-die SoC designs, helping deliver higher performance and lower power across both “cost-down for mass” and “feature-up for premium” segments.
Any re-use permitted for informational and non-commercial or personal use only.













